Mapping Software and GIS Glossary
Geocoding is the process of converting location descriptions, such as addresses or coordinates, into geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude) that can be plotted on a map. This process allows businesses, researchers, and everyday users to visualize and analyze spatial data. There are several types of geocoding, each suited to specific needs, ranging from text-based input to batch processing.
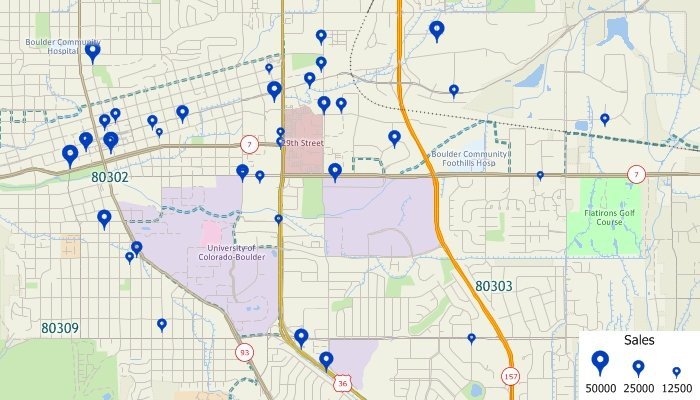
What is geocoding? This map shows customer addresses geocoded onto a map as point locations. All of the original source data, such as sales volume, are also available for mapping and labeling the geocoded point features.
Text-based geocoding involves using common location descriptors such as:
This is the most common form of geocoding and is widely used in navigation apps, logistics, and demographic analyses.

An address (97 Chestnut St) geocded to the approximate location, an intersection (Charles St & Branch St) geocoded to the center of the intersection, a postal code (02108) geocoded to a ZIP Code, and a city (Boston MA) geocoded within the city boundary
The accuracy of text-based geocoding depends on the method and data used to identify locations. Common types of text-based geocoding include:
Each method has its use case, with rooftop accuracy being the gold standard for applications requiring precision.

Addresses are placed along the street based on the address range

Addresses are placed along the street based on the address range and offset to the appropriate side of the street

Addresses are placed based on the physical locations of the buildings
Grid-based geocoding assigns locations to pre-defined grids, enabling spatial precision and consistency. Popular grid-based systems include:
Grid-based geocoding is particularly useful for rural areas, disaster relief, and logistics in regions without formal addressing systems.

What3Words grid where every 3-meter square is identified by three words

Uber H3 hexagonal grid
Coordinate geocoding converts specific longitude and latitude pairs (or x/y values) into points on a map. Examples include:
Coordinate geocoding is essential for GPS navigation, geospatial analysis, and applications that rely on precise positioning.

Precisely geocodeds latitude/longitude locations
Reverse geocoding is the opposite of geocoding: it converts geographic coordinates into human-readable descriptions. For example, the coordinates (40.748370, -73.984640) return the address "Empire State Building, New York, NY."
Applications of reverse geocoding include:

Batch geocoding is the process of geocoding multiple locations at once. This is particularly useful for businesses and organizations handling large datasets, such as:
Batch geocoding tools streamline workflows, saving time and ensuring accuracy in large-scale mapping projects.

Geocoding is a critical component of modern mapping and analysis. It enables businesses, governments, and researchers to better understand spatial relationships, optimize operations, and make informed decisions based on location data.
Geocoding technology offers significant benefits across various sectors, enhancing data accuracy and enabling sophisticated spatial analyses. Several studies and reports highlight its impactful applications:
The National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) utilizes
geocoding to link survey participant addresses with geographic
information, enriching data analysis. This integration allows
researchers to combine neighborhood and ecological information
with individual survey data, expanding the use of geocoded data
to improve public health.
FCSM Home
In urban planning, geocoding enables the integration,
mapping, and analysis of geographic data, facilitating efficient
data management and spatial analysis. For instance, the Chicago
Police Department's Information Collection for Automated Mapping
(ICAM) system uses geocoding to produce maps of reported
offenses in specific areas, aiding in crime pattern analysis and
resource allocation.
Office of Justice Programs
Geocoding serves as a foundational element in geographic
information systems (GIS), efficiently indexing spatial data by
converting geographic coordinates into concise strings. This
process supports various applications, including environmental
monitoring, transportation planning, and resource management.
IEEE Xplore
Maptitude Mapping Software gives you all of the tools you need to geocode and analyze your data. Included with Maptitude is:
With Maptitude you can locate unlimited records, map your location data, build sales territories from customer addresses, and analyze your mapped pushpins. Maptitude does not have any additional fees for geocoding, allowing you to plot large databases of coordinates at minimal cost.

Home | Products | Contact | Secure Store