|
|
|
TransCAD is the only software package that fully integrates GIS with demand modeling and logistics functionality. Unlike other GIS software products, application modules in TransCAD are fully integrated with GIS functions for improved performance and ease of use. TransCAD can also solve problems of virtually any size. This makes TransCAD ideal for many types of transportation applications including:
Network analysis models are used to solve many types of transportation network problems:
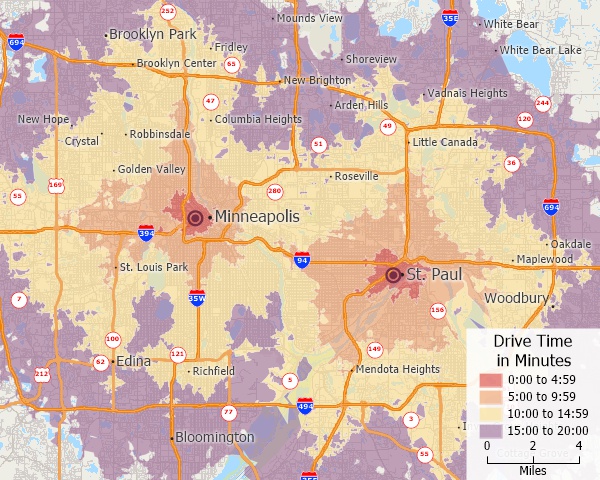
Five-minute interval drive-time rings around two locations
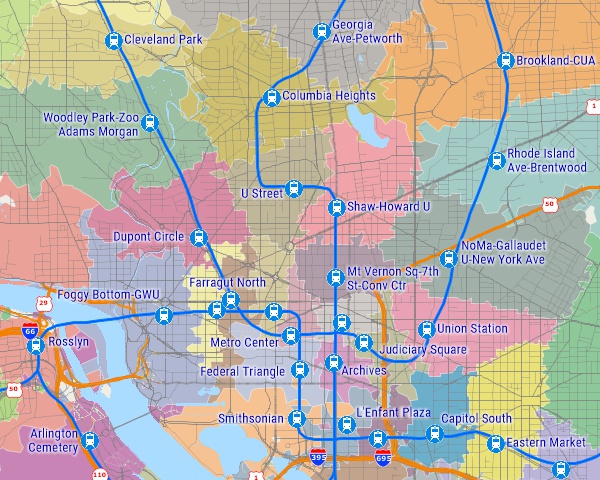
Territories based on walking distance to nearest subway station
Transportation planning and travel demand models are used to predict changes in travel patterns and the utilization of the transportation system in response to changes in regional development, demographics, and transportation supply. TransCAD is the only planning package that is GIS-based and fully integrates GIS and planning tools for trip generation, trip distribution, mode split modeling, and traffic assignment. TransCAD includes all of the traditional UTPS models, quick response models with reduced data requirements, and advanced disaggregate demand models.
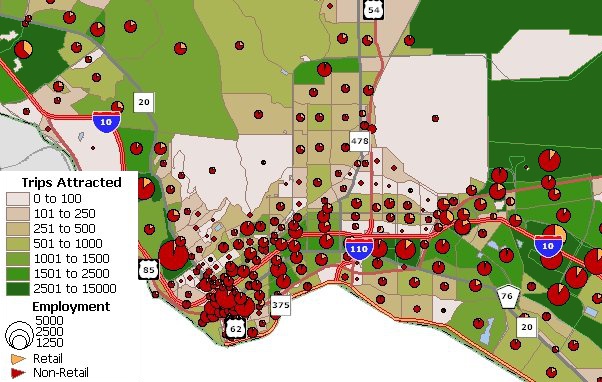
Trip production and trip attraction models estimate trip from or to zones
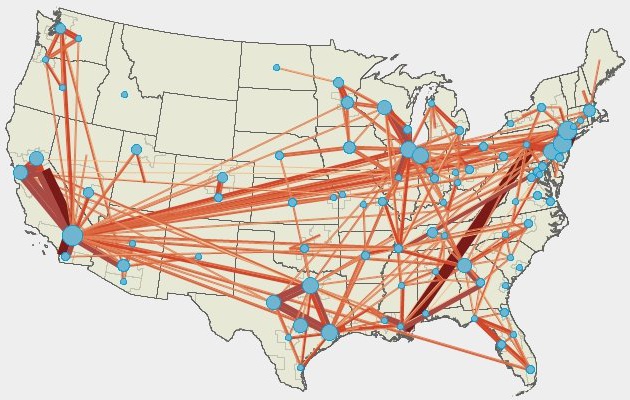
Trip distribution models predict flows among origins and destinations
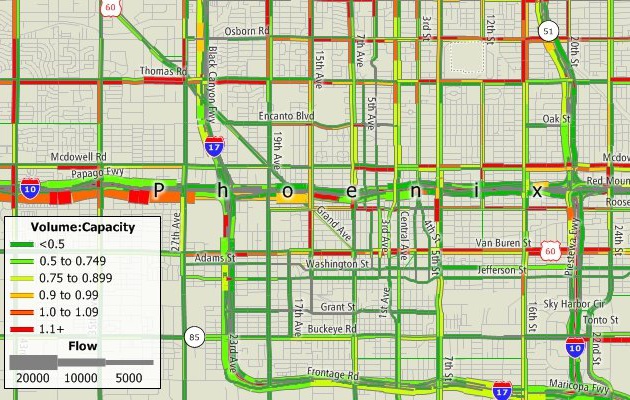
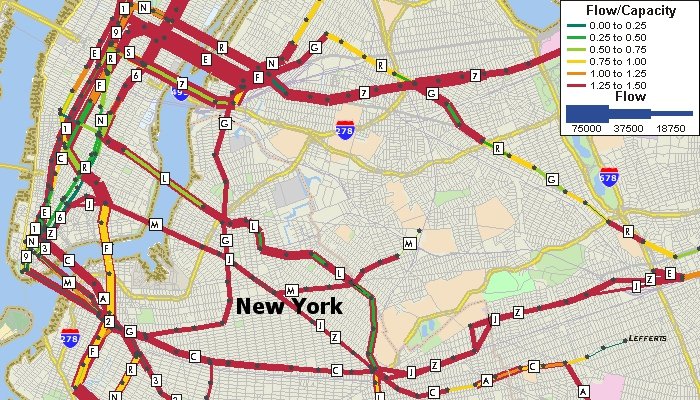
Traffic assignment models estimate flow on a network
For more information, see the Planning and Travel Demand page for a comprehensive overview of the travel demand capabilities of TransCAD.
TransCAD also has special tools and procedures for creating and working with transit networks. Transit fares can be specified as either flat or zonal. Using transit networks and fare structures, you can solve shortest path problems and calculate transit path attributes (i.e. skims). You can also have separate and fully integrated networks for non-motorized travel modes. For example, you can include pedestrian links when doing transit network analysis.
Transit networks can also be used for performing transit assignment. You can estimate the number of passengers that utilize links in a transit network as a function of transit level of service. These models produce link level and aggregate ridership statistics. TransCAD includes an array of sophisticated transit network assignment procedures.
TransCAD is the only GIS with specific extensions for public transit. TransCAD can perform data management for complex transit systems and has applications in customer information systems, scheduling, and marketing.
TransCAD includes a comprehensive library of logistics procedures that apply to all modes of transportation and can be used to solve a variety of logistics problems.
Vehicle Routing/Dispatching
TransCAD provides a rich set of tools that solve various types of pickup and
delivery routing problems. These tools are used to prepare input data,
solve the routing problem, and provide tabular and graphical output of
the resulting routes and vehicle schedules. The TransCAD procedures can
solve many variations on the classic vehicle routing problem, including
restrictions on the time when stops can be made, the dispatching of
vehicles from multiple depots, and the use of non-homogeneous vehicle
fleets. The vehicle routing procedure in TransCAD is also capable of
solving problems involving mixed pickup and delivery. Once a solution is
found and the results displayed graphically, users can edit the routes
interactively by adding or removing stops. Once stops have been added or
removed, users can perform a re-optimization of the route so as to
minimize time window violations.
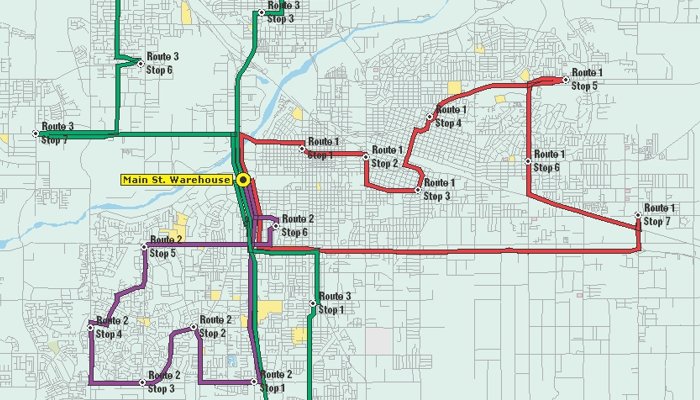
Arc Routing
Arc routing problems are a class of problems that involve finding efficient
ways to travel over a set of links in a transportation network. Arc
routing has a large number of public and private sector applications,
including street sweeping, solid waste collection, snow plowing, mail
delivery, and other door-to-door operations. In a typical arc routing
problem, people or vehicles are dispatched from one or more depots to
traverse a set of service links. The result of an arc routing problem is
a set of one or more routes that cover all the service links with the
minimal amount of deadheading.
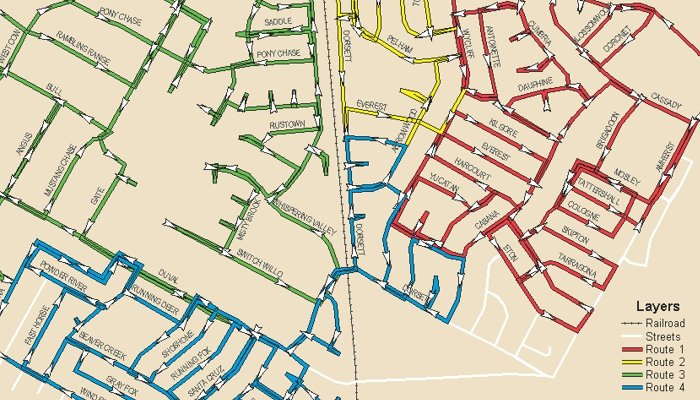
Network Flow and Distribution Analysis
TransCAD includes a set of procedures for solving network flow problems. These
problems involve efficient delivery of goods or services, and arise in
transportation and many other contexts.
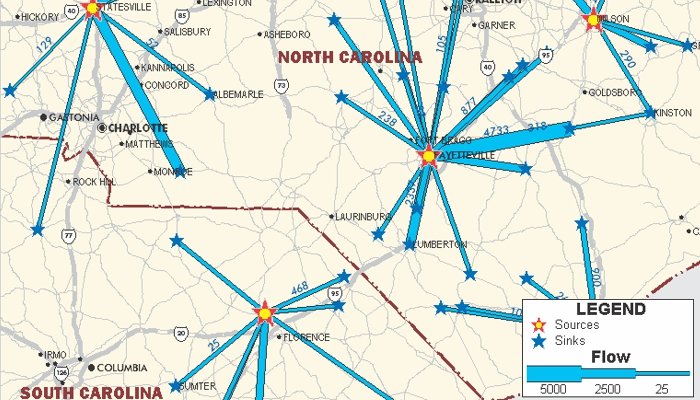
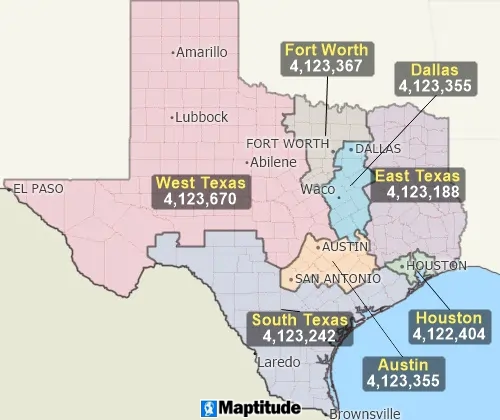
TransCAD procedures for regional partitioning, clustering, and facility location have broad applications in transportation and marketing. Clustering routines assemble customers, facilities, or areas into groups that are compact and can be serviced efficiently. Districting models group Census tracts, ZIP Codes, counties, or other regions into territories that are compact and balanced. Location models evaluate the costs and benefits of any number of proposed facility locations.
Territory Definition
TransCAD provides powerful automated procedures for defining
territories:
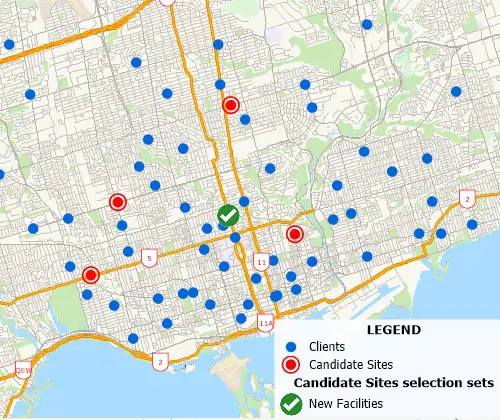
Site Location Analysis
Site location problems involve choosing the best location for
one or more facilities from a set of possible locations. TransCAD can
address virtually all types of location problems. For example: